Data Fusion
By Catalina9
Data fusion is the process of integrating multiple data sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than what is provided by any individual data source. Data fusion is the process of getting data from multiple sources in order to build more sophisticated models and understand more about a project. It often means getting combined data on a single subject and combining it for central analysis. In airport operations data fusion is to obtain reports from multiple sources such as weather information, NOTAM, hazards, incidents or accidents and analyze in a single source Statistical Process Control (SPC). Data fusion is to analyze how a change in one source affects, or trickle down to the other sources within a system. A Safety Management System is a Data Fusion System.
 |
| Data Fusion is the data comprehension process. |
Data supporting an SMS is always available but needs to be captured before being put into use. Capturing data is more than receiving reports, it is also to conduct research to extract information. Just data in itself is not an asset to a safety management system, but within a Data Fusion System it becomes an invaluable asset. Data collected must first be transformed into information. When information is consumed, through any of the five senses, information becomes knowledge. With knowledge comes comprehension of one, two or more systems within a Data Fusion System.
SMS is a businesslike approach to safety. In a business data equals cash, which always is there, but unless captured it is not a source to be used in operations. Data to an SMS Enterprise is just as much value to operations as what cash is to a business. During the pre-SMS days, accident investigation focused on pilot errors, or what task a person failed to do. At some point after the 1956 Grand Canyon disaster, problem solvers decided that the pilot, or a human was the problem. In 1956 when two aircraft crashed over the Grand Canyon, the probable cause was not determined to be what the pilots failed to do, but that the pilots did not see each other in time to avoid the collision du to intervening clouds, visual limitations due to cockpit visibility, preoccupation with normal cockpit duties, preoccupation with matters unrelated to cockpit duties such as attempting to provide the passengers with a more scenic view of the Grand Canyon area, physiological limits to human vision and insufficiency of enroute air traffic advisory information. Probable causes for the disaster included human factors, organizational factors, supervision factors and environmental factors. The probable cause was based in data fusion and how data from multiple sources trickles down to one outcome.
Data Fusion is where data become available
without subjective random selection
For data fusion to functioning as intended, data needs to be tied to an open-source project. Within the SMS an open-source project is where data is freely available, it is shared, and it is decentralized. No single enterprise, being large, medium, or small, has enough data available within its own organization to apply a data fusion system in their operations. Data fusion is in essence to reverse the reactive data collection process when data, or hazards must be visible for collection, to applying a proactive collection process where data available is trickling into multiple systems.
Data collection is a major task to operate with an effective SMS. There is an expectation that the aviation industry collects its own data and apply that data to their operations. The aviation industry also expects that data collected by one enterprise is not applicable, or directly shareable, with another enterprise within the same industry. SMS guidance material states that “Your organization must develop policies, processes and procedures that support your unique operating requirements and that fit the size and complexity of your organization.” When SMS first was implemented by regulations, these types of statements were incorrectly interpreted that their own data would only be applicable to their own organization and that nobody else should benefit from their discoveries.
The same misconception was for the Accountable Executive (AE), that their only role was to have control of the financial and human resources that were necessary for their activities and operations. When in fact, the role and responsibilities of an AE is to be accountable on behalf of an enterprise to meet all the requirements of the regulations. In other words, an AE must not only have knowledge of all regulations for compliance, but also know and comprehend what processes are necessary for compliance and what processes drifts towards non-compliance. An AE without a confidential adviser stands no chance to maintain this compliance requirement.
All data for an SMS system is already out there, but needs to be captured, filtered, and analyzed. Capturing data comes in many shapes and forms. Just as cash in a business comes in bills, coins or plastic, data in an SMS comes as hazards, incidents, or emotions. Capturing cash is by affecting human behavior in purchasing patterns, expectations, and social acceptance. Capturing data for SMS is generally a reactive process and is not “cashed in” until after an event. The capture of SMS data will benefit greatly by learning from the advertising and marketing industry by affecting human behaviors to recognize their own patterns, expectations, and social acceptance within and SMS enterprise, or in other words, changing their organizational culture to a just-culture. Within a just-culture is when data fusion becomes available. Filtering data is not associated with subjective selection of data, but it is to filter data into their pre-established safety critical areas and safety critical functions. Filtered data is then analyzed in a Statistical Process Control (SPC) System, where emotions and subjective randomization are eliminated from the equation. When SPC is eliminated from the analysis with a reaction to a statistical trend, there is a tendency for overcontrol, and applying one or two events as a trend, which again leads to a greater hazard than the hazard itself.
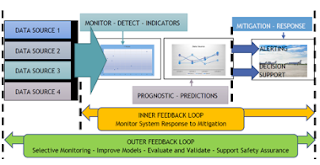 |
Data Fusion is tracking, mapping and loop closure. |
A Data Fusion System is a system where there is tracking, mapping and loop closure. It is also a system where data trickling from one system into another system affects both the system it is trickling from and the system it is trickling into, which also is defined as organizational drift. The tools to implement a Data Fusion System into SMS is by applying a data collection tool that your enterprise has full control over. It is to conduct research, development, project planning and work directed toward the innovation, introduction, and improvement of processes. Data Fusion is a condition, while the audit result is the symptom.
Catalina9







